COMPUTATIONAL GENOMICS
THE "HOW" OF SCIENCE

TECHNOLOGY IN BIOINFORMATICS

The VISTA family of tools is one of the only comparative genomic services that integrates the alignment and visualization of multiple genomes for analysis. The family of tools uses alignment techniques and a curve visualization strategy to identify and align sequences. The technology also adds a mapping component for the multiple genomic sequences that are being studied in the analysis. The VISTA family of tools also seeks to accurately predict where functional signals in the genome into consideration such as the site where the transcription factor binds.

This tool is especially useful in visualizing multiple genomes to scale. The browser allows users to see the annotated genomes in a visual interface.

PLINK is a free software that is focused on analyzing the association between whole-genome studies. Like SNPTEST, its goal is to perform the statistical calculations to produce the mathematical results of GWAS.

BLAST technology is a bioinformatics software designed specifically to analyze genes. The software searches for regions of local homology within the sequenced gene. Like the technology developed prior, the BLAST technology uses statistical information and a sequence database to calculate the significance of each nucleotide or protein alignment. Therefore, BLAST technology can be used specifically to interpret evolutionary relationships between sequences.

FASTA was the first of many bioinformatics tools that analyzes genes. The original FASTA program was designed to complete DNA searches, alignment analysis of multiple genomes, and strategically comprehend the significance of each dataset.

Gene Quiz works by comparing sequences of bases with several similar databases including PDB, SWISS-PROT, PIR, PROSITE, and TrEMBL. Using an algorithm, the program analyzes similarities in the data in order to predict functions and clusters proteins accordingly. The data is presented in a table that provides predictions of protein function, gene names, and links to databases that contain more information.

Pedant automatically analyzes genome sequence for protein function. The prediction of cellular roles and functions is made by cross-referencing the information provided with databases in Pfam, BLOCKS, and PROSITE databases. Protein functions are manually assigned categories based on the Functional Catalogue (FunCat)

Ergo is a genome annotation platform where the annotation is completed by combining next-generation sequencing data and genome assembly to draft a sequence of genes. The ERGO platform is highly accurate because it structures the entire genome instead of only looking for sequence similarities to predict protein functions.

MapView: The Map Viewer contains information necessary to understand how to map, view, and sequence genomes.

Ensembl: The Ensembl project contains sequencing references for the genomic profiles of many vertebrates and eukaryotic species, which is especially helpful in the computational analysis of multiple genomic sets.

This browser is open- sourced online and holds sequences and annotation tools for a large collection of genomes.

SNPTEST is a computer software that is designed to analyze multiple genomes (which are obtained during the GWAS) and find any possible correlations between diseases and gene mutations.

MPSS uses very similar techniques as SAGE: The mRNA is converted into cDNA strands. The cDNA strands are bonded with an oligonucleotide tag. Fluorescent-labeled probes are used to produce a signature sequence of 16-20 base pairs, which is used to identify each fragment (This step diverges from the methods used in SAGE). Fluorescent imaging captures a parallel image of the DNA by interpreting the signal from all of the beads
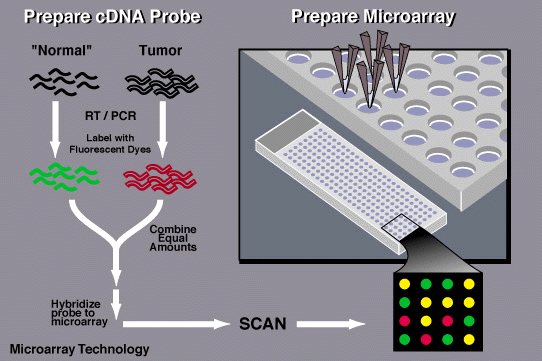
A DNA microarray is a technique that scientists use to determine the expression of certain genes and whether they contain mutations. The microarray is a microscopic plate printed with dots containing the known sequences of DNA in specific places on the plate.
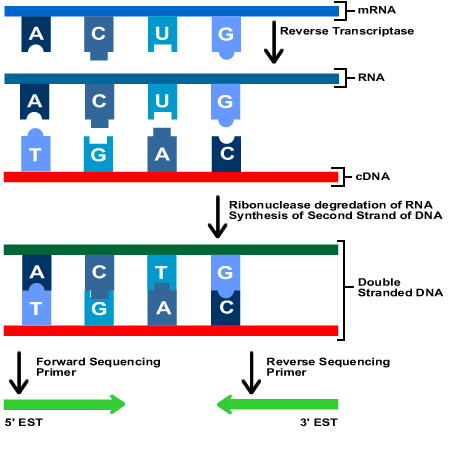
ESTs are small DNA sequences that represent genes expressed in certain cells or tissues in different organisms. Scientists use these bits of DNA to find complementary strands in a portion of chromosomal DNA. The idea is that the part of the chromosome that codes for the same proteins as the EST sample will bind to the sample, making the process of identifying those genes in the large chromosome more efficient

Serial analysis of gene expression, or SAGE, is an experimental technique that scientists use to produce a snapshot of mRNA in a sample population. The SAGE method isolates unique sequence tags of mRNA and links them into a large DNA molecule for sequencing.